
Cybersecurity is the process of saving internet-linked systems such as software, hardware, and data from cyber threats. It is employed by people and companies to safeguard data centers and other computerized systems from unauthorized access.
An adequate cybersecurity strategy can deliver a robust security stance against vicious attacks created to destroy, access, delete, alter, or extort an organization’s or individual’s systems and sensitive information. It also plays a crucial role in stopping attacks intended to disable or interrupt the functioning of systems or devices.
Here’s what you need to know about cybersecurity.
Why is cybersecurity necessary?
With the number of devices, users, and programs in the current business growing along with the quantity of data — broadly of which is confidential or sensitive — cybersecurity is more essential than ever. However, the complexity and volume of cyber attackers and attack methods compound the situation even further.
Without a good cybersecurity process on the spot– and staff adequately prepared on security’s most promising techniques — malicious players can bring a business’s functions to a sharp halt.
What are the aspects of cybersecurity and how does it function?
The cybersecurity area can be split down into many distinct areas, the coordination of which within the community is important to the victory of a cybersecurity program. These areas possess the following:
- Application security.
- Operational security.
- Information or data security.
- Cloud security.
- Critical infrastructure security.
- Physical security.
- Network security.
- Disaster recovery and business continuity planning.
- End-user education.
Supporting cybersecurity in a continually growing threat terrain is a challenge for every community. Conventional reactive techniques, in which resources were set toward defending systems from the largest learned threats while unpopular threats were unprotected, are no longer a pleasing tactic.
To keep up with varying security threats, a more aggressive and adaptive system is essential.
What are the advantages of cybersecurity?
The advantages of executing and defending cybersecurity methods include the following:
- Business protection against data breaches and cyberattacks.
- Protection of networks and data.
- Enhanced recovery time after a violation.
- Deterence of unauthorized user access.
- Regulatory compliance.
- Security for end users and endpoint devices.
- Business continuity.
- Enhanced confidence in the company’s prestige and faith in partners, stakeholders, developers, customers, and employees.
What are the distinct kinds of cybersecurity threats?
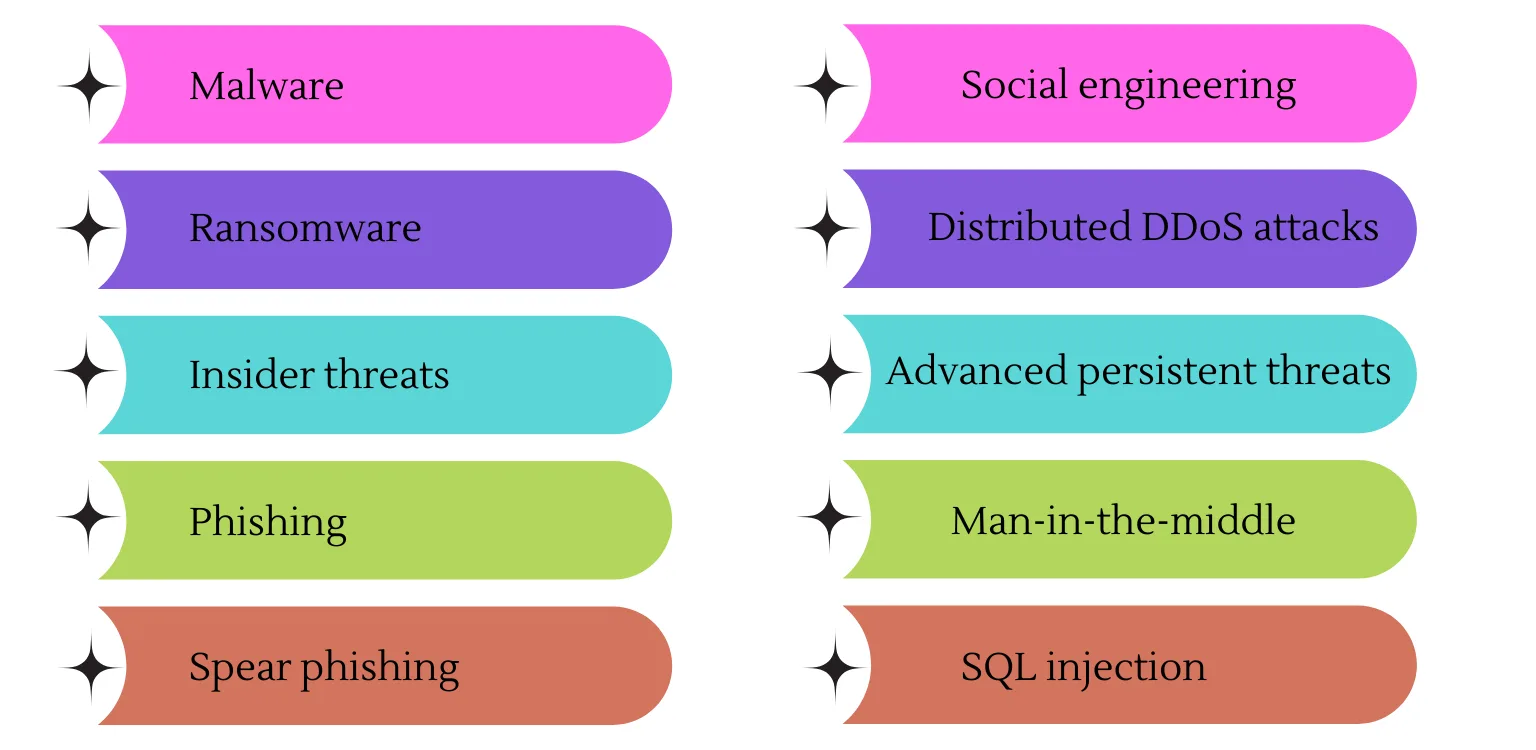
Holding up with security trends, new technologies, and threat intellect is a difficult task. It’s essential to safeguard information and other aids from cyber threats, which carry multiple forms. Kinds of cyber threats include the following:
- Malware is a state of vicious software in which any program or file can be employed to break a user’s computer. Distinct kinds of malware include Trojans, viruses, worms, and spyware.
- Ransomware is a form of malicious software in which an attacker encrypts a victim’s system files, effectively locking them, and then demands a ransom payment to restore access by decrypting the files.
- Phishing, a subset of social engineering, involves sending deceptive emails or text messages that appear to come from trusted or familiar sources. These attacks are often carried out randomly and are designed to steal sensitive data, such as login credentials or credit card details.
- Insider threats are safety violations or failures induced by humans — for instance, contractors, employees, or customers. Insider threats can be negative or careless.
- Social engineering is a type of attack that depends on manipulating human behavior. It deceives individuals into bypassing security protocols to reveal confidential information.
- Spear phishing is a kind of phishing that includes an intentional target organization, user, or business.
- Distributed DDoS attacks are those that involve multiple systems overwhelming the traffic of a specific target, such as a server, website, or network resource. These attacks flood the target with excessive messages, connection requests, or data packets, which can significantly slow down or crash the system, making it inaccessible to legitimate users.
- Advanced persistent threats (APT) is a lengthy aimed invasion in which an assailant enters a network and stays hidden for long periods. The purpose of an APT is to steal info.
- Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks are a form of eavesdropping in which an attacker secretly intercepts and transmits messages between two parties, making them believe they are directly communicating with one another.
- SQL injection is a technique used by attackers to gain access to a web application’s data by inserting malicious SQL code into a database query. This attack allows unauthorized access to sensitive information and enables the execution of harmful SQL commands.
Other typical kinds of attacks include drive-by-download attacks, botnets, cross-site scripting attacks, keyloggers, worms, exploit kits, vishing, credential stuffing attacks, malvertising, and zero-day exploits.
There are multiple kinds of malware, including viruses and ransomware.
How is automation used in cybersecurity?

Automation has become an essential element in keeping businesses safe from the rising number and complexity of cyber threats. Employing machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) and in places with high-volume information creeks can help enhance cybersecurity in the ensuing three major classes:
- Threat detection. AI platforms can explore data and identify renowned threats, as well as indicate novel dangers that employ newly found attack methods that circumvent standard security.
- Human augmentation. Security pros are usually packed with repetitive tasks and alerts. AI can help eradicate alert exhaustion by automating big data analysis and automatically triaging low-risk alarms and other repetitive duties, liberating humans for more refined tasks.
- Threat response. AI platforms are designed and automatically pass safety protections.
Other advantages of automation in cybersecurity include malware classification, attack classification, compliance analysis, traffic analysis, and more.

Advances in cybersecurity technology
As more latest technologies evolve, they can be used in cybersecurity to advance safety techniques. Several emerging technology trends in cybersecurity include the following:
- Security automation through AI. While machine learning and AI can help detractors, they can also be employed to automate various cybersecurity tasks. AI is good for exploring extensive data volumes to determine practices and for creating forecasts on possible threats. AI tools can also offer potential areas for exposure and determine patterns of uncommon behavior.
- Zero-trust architecture. Zero-trust principles operate on the assumption that no user or device should be trusted by default without proper verification. Adopting a zero-trust model can help decrease the occurrence and impact of cybersecurity breaches, while also offering additional security advantages.

