JavaScript, as a language, is known for its single-threaded nature, meaning it can only execute one line of code at a time. Despite this, JavaScript has an impressive ability to handle multiple tasks simultaneously through asynchronous behavior. Asynchronous JavaScript is what enables tasks like network requests, timers, and file I/O to run without blocking the main thread. This approach is essential for creating responsive, performant applications, especially on the web, where waiting for a task to complete could otherwise mean freezing the user interface (UI).
1. The Basics of JavaScript’s Execution Model
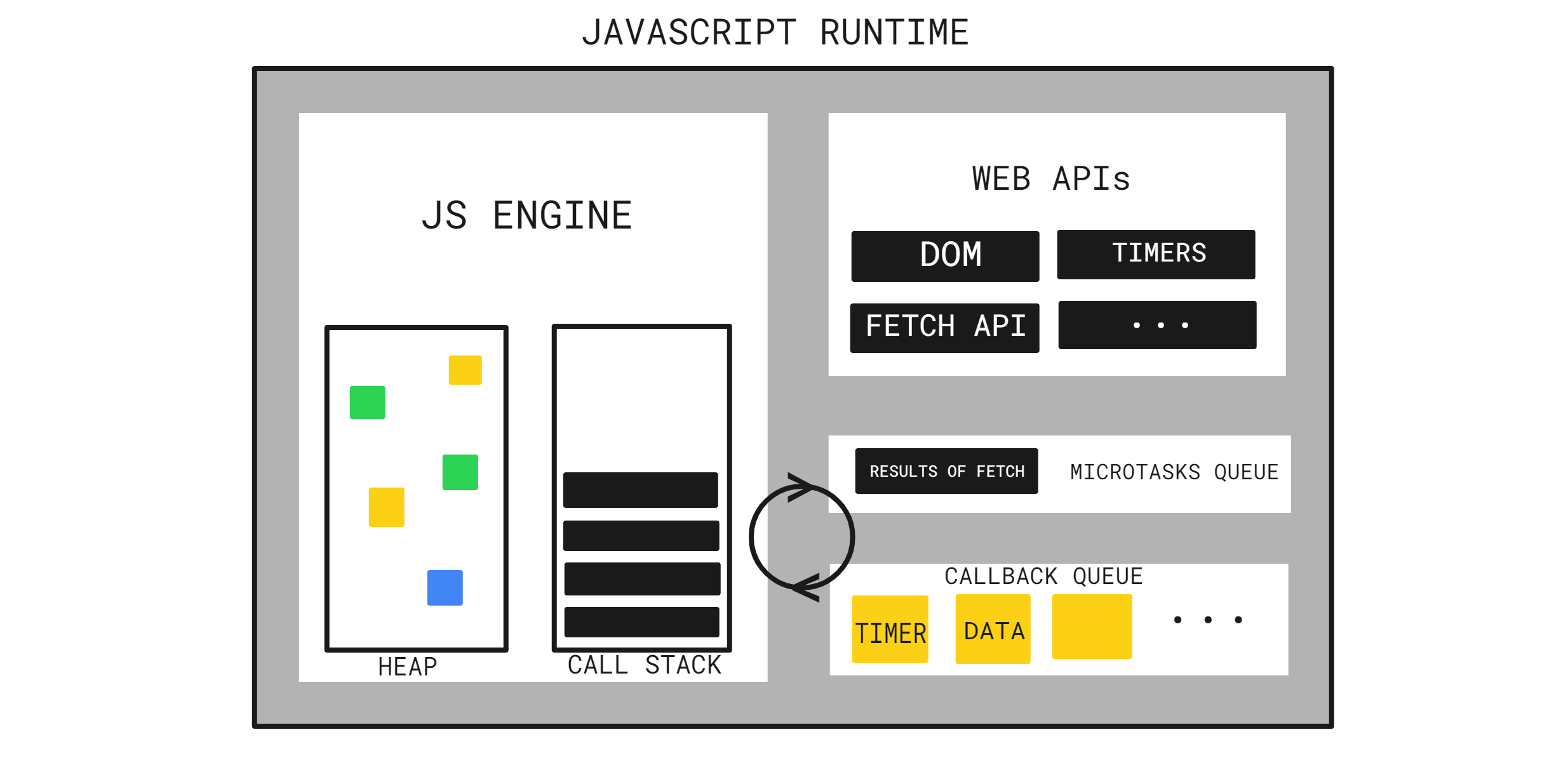
To understand asynchronous behavior, it’s essential to grasp JavaScript’s execution model. JavaScript uses a single-threaded, non-blocking, event-driven model, meaning:
- Single-threaded: JavaScript can handle one task at a time in a linear manner.
- Non-blocking: Rather than waiting for long-running tasks (e.g., network calls) to finish, JavaScript allows other code to run in the meantime.
- Event-driven: JavaScript relies on events and callbacks to manage tasks that happen at different times.
Because JavaScript is single-threaded, it runs synchronously by default—executing one line of code after another. However, when there’s an operation that would take too long to finish, such as fetching data from an API or reading a file, JavaScript doesn’t block other operations. Instead, it handles these through asynchronous mechanisms, which we’ll cover next.
2. The Call Stack
The call stack is the first step in understanding JavaScript’s execution. It’s a data structure that keeps track of function calls in the order they need to be executed. When JavaScript encounters a function, it adds it to the stack. Once the function finishes, it’s removed from the stack, allowing JavaScript to continue executing other code.
In synchronous code, functions are added to the call stack and removed one after the other. However, asynchronous code introduces additional complexity. Long-running operations cannot remain on the stack, as they would block other tasks. This is where the Web APIs and event loop come into play.
3. Web APIs: Handling Asynchronous Tasks
Modern browsers provide various APIs (Web APIs) for handling time-consuming tasks, such as:
- setTimeout() and setInterval(): For delaying execution
- XMLHttpRequest and Fetch API: For making network requests
- DOM events: For handling user interactions like clicks or keyboard inputs
When JavaScript encounters one of these APIs, it offloads the task to the Web API environment provided by the browser. For example, if you set a timer with setTimeout(), JavaScript passes it to the Web API, and the main thread continues running other code. When the task completes (e.g., the timeout expires), it’s placed in the Callback Queue, waiting to be added back to the call stack.
4. The Event Loop: The Key to Non-Blocking Code
The event loop is at the heart of JavaScript’s asynchronous behavior. Its job is to monitor the call stack and the callback queue. Here’s how it works:
- Check the call stack: If it’s empty, the event loop looks at the callback queue.
- Move tasks: If there’s a task in the callback queue and the call stack is empty, the event loop moves the task from the queue to the stack for execution.
- Repeat: This process repeats continuously, allowing JavaScript to handle asynchronous tasks without blocking.
The event loop ensures that the code runs efficiently, without freezing or slowing down the browser. This setup is what enables JavaScript to perform non-blocking operations despite being single-threaded.
5. Callback Functions: The Foundation of Asynchronous Code
The first and simplest approach to asynchronous programming in JavaScript is with callbacks. A callback is a function passed as an argument to another function and is executed once an operation completes. For example:
Here, fetchData takes a callback function and uses setTimeout to simulate a delayed response. Once setTimeout completes, it runs the callback function, logging “Data received!” to the console.
While callbacks are effective, they can lead to a problem known as callback hell, where nested callbacks make the code hard to read and maintain. To address this, JavaScript introduced promises.
6. Promises: A More Manageable Approach
A promise represents a value that will be available in the future. It’s an object that can be in one of three states:
- Pending: The initial state, where the result is not yet available.
- Fulfilled: The operation completed successfully, and the result is available.
- Rejected: The operation failed, and an error is available.
Promises simplify asynchronous code by allowing you to chain operations together, avoiding deeply nested callbacks. Here’s an example:
Using .then() and .catch(), we can handle the promise’s success and error cases in a cleaner, more readable way. Promises transformed asynchronous JavaScript, providing a structured way to handle sequential asynchronous operations.
7. Async/Await: Simplifying Asynchronous Code Further
While promises improved asynchronous programming, async/await makes it even easier by allowing asynchronous code to look more like synchronous code. async functions return a promise, and await pauses the function’s execution until the promise resolves. Here’s how it works:
In this example, displayData is an async function that calls fetchData. By using await, we can pause the function until fetchData resolves, making the code more readable and eliminating the need for .then() chains.
Error Handling with Async/Await
With async/await, error handling is straightforward. You can use try...catch blocks to handle rejected promises, making it easier to manage errors in asynchronous functions.
8. Microtasks and Macrotasks: A Deeper Look at the Event Loop
In JavaScript, tasks are categorized into macrotasks and microtasks:
- Macrotasks: Tasks like
setTimeout,setInterval, and DOM events. - Microtasks: Tasks like
Promise.then()andprocess.nextTick(in Node.js).
The event loop prioritizes microtasks over macrotasks, meaning that after each macrotask, the event loop will execute all microtasks before moving on to the next macrotask. This behavior is crucial in managing the timing and order of asynchronous code execution.
9. Real-World Applications of Asynchronous JavaScript
JavaScript’s asynchronous behavior is essential in building fast, responsive applications. For example:
- Fetching Data from APIs: Making HTTP requests to APIs for data (e.g., using the
fetch()API). - User Interface Interactions: Handling button clicks, mouse movements, and other UI events.
- Timers and Animations: Delaying actions or creating animations using
setTimeoutorsetInterval.
By leveraging async/await, promises, and the event loop, JavaScript can handle these tasks without blocking the main thread, creating smooth and interactive user experiences.
10. Conclusion
JavaScript’s asynchronous behavior, despite its single-threaded nature, allows developers to build powerful applications that don’t freeze or slow down. Through mechanisms like callbacks, promises, async/await, and the event loop, JavaScript efficiently handles time-consuming operations in the background.
